VIMS professor receives VA Outstanding Scientist Award
Professor Robert J. Diaz of the Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary, has received one of four Outstanding Scientist awards for Virginia for 2010.

The award is bestowed annually by the Governor's Office and the Science Museum of Virginia to honor those who have excelled in research and commitment to science, and whose contributions to scientific research have extended the boundaries of their own and other fields. Award recipients are selected by a distinguished panel of internationally renowned Virginia scientists.
Governor Bob McDonnell will present the awards during a legislative reception at the Museum on the evening of January 27.
Diaz, in his 32nd year as a professor of Marine Science at VIMS, is the international “go-to guy" for information on the ecological effects of low-oxygen “dead zones” in the world’s oceans and Chesapeake Bay. As to why dead zones are important, Diaz uses a quote from the American Lung Association: “If you can’t breathe, nothing else matters.”
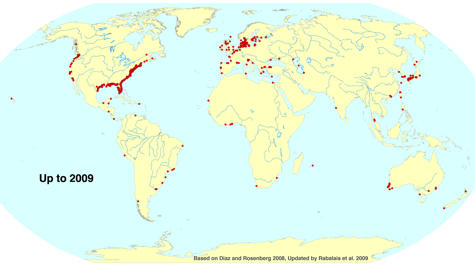
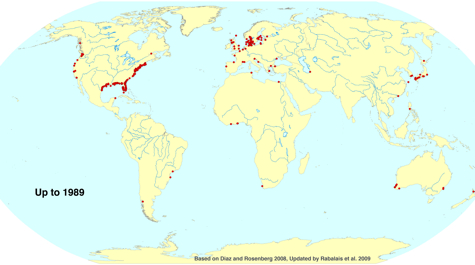
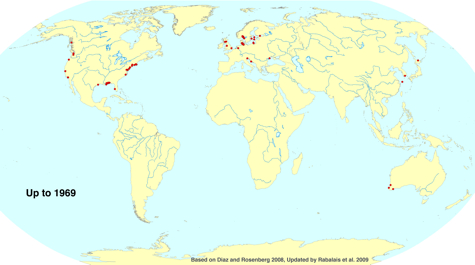
Diaz’s work highlights dead zones as barometers of global environmental stewardship, as their severity and duration correspond to nutrient inputs from human activities. He made his name with a 1995 article co-written with Swedish scientist Rutger Rosenberg that provided the first-ever global tally of dead zones. In 2008, Diaz and Rosenberg updated the status of dead zones for the international journal Science, and in 2009, Diaz was lead contributor to a special dead zone report to the White House Committee on the Environment and Natural Resources. Last year he briefed Congress on the ecological effects of the chemical dispersants used in the Gulf oil spill, and on the oil’s potential effects on dead zones in the Gulf.
Dr. John Wells, Dean of the School of Marine Science at W&M and Director of VIMS, says "As the international expert on this issue, Bob is a truly worthy recipient of the Governor’s award. It reflects his many years of research to understand the scientific basis of dead zones, and his success in bringing the problem—and potential solutions—to the world’s attention."
Diaz’s work shows that the number of dead zones has increased worldwide by more than a third between 1995 and present, and that dead zones now rank with over-fishing, habitat loss, and harmful algal blooms as global environmental problems. A dead zone underlies much of the main-stem of Chesapeake Bay each summer, occupying about 40% of its area and up to 5% of its volume.
Dr. Roger Mann, Director of Research and Advisory Service at VIMS, says "Bob has risen to the challenge of communicating a global and very complex problem to the public. His work challenges those who have an investment in a sustainable biosphere—and that is all of us—to be more responsible in our use of natural resources.”
Diaz’s global dead-zone database now appears as a layer in Google Earth, and forms the backbone of an interactive website developed in partnership with the World Resources Institute.
Academic and Scholarly Achievements
During his time at VIMS, Diaz has mentored more than 75 graduate students, many of whom have gone on to leading positions in academia, government, and industry. He has authored or co-authored 20 scientific publications in the last 5 years alone, and has served on countless advisory bodies, including the United Nations’ technical advisory panel on nutrient reduction to reduce hypoxia, and the Environmental Protection Agency’s Science Advisory Board.

Diaz has also provided advisory service to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, the National Marine Fisheries Service, the Department of the Interior, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, the Hudson River Foundation, and local and national Sea Grant offices.
Closer to home, Diaz has helped the Virginia Department of Environmental Quality develop water-quality standards for the Commonwealth, and advised the agency on technologies for accurately measuring dissolved oxygen. He has also advised local industry and military organizations on “bio-fouling” of Navy ships, and plays a key role in scientific research concerning the environmental impacts of proposed oil and gas exploration off Virginia’s coast. He is also a frequent contributor to VIMS’ public outreach efforts, having spoken to citizens groups and school children throughout tidewater Virginia.
Diaz joins the late Dr. William Hargis and professors emeriti Jack Musick and Eugene Burreson in receipt of a Governor's award from the Science Museum. Hargis, Musick, and Burreson were honored with Virginia's Lifetime Achievement in Science Award.