Dead Zones and Climate Change
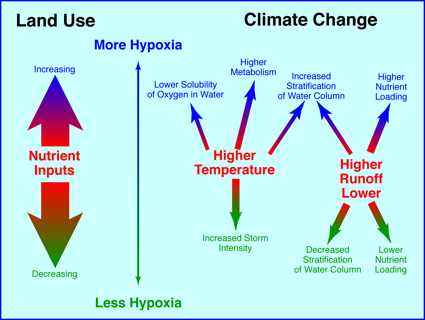
Evidence suggests that several projected outcomes of global climate change will act to increase the prevalence and negative impacts of low-oxygen dead zones:
- Warmer waters hold less oxygen than cooler water, thus making it easier for dead zones to form
- Warmer waters will increase metabolism of marine creatures, thereby increasing their need for oxygen
- Warmer temperatures and increased runoff of freshwater will increase stratification of the water column, thus further promoting the formation of dead zones
- Increased runoff will also increase nutrient inputs into coastal waterbodies
On the other hand, projections of more intense tropical storms and lower runoff would act to decrease stratification and thus make dead zones less likely to form or less pronounced if they do form.